 As discussed in our previous post Image Files - Formats and Uses, JPEG image files are the most commonly used digital image format. They are universally compatible with just about every usage and storage medium imaginable, allowing for high quality photographic images at manageable sizes. Digital image files including JPEGs are often stored, transfered and used directly from today's most popular digital storage devices and mediums. These include memory cards (such as those found in cameras), memory sticks, cards, portable hard drives, internal hard drives, network storage devices, as well as DVDs and CDs.
As discussed in our previous post Image Files - Formats and Uses, JPEG image files are the most commonly used digital image format. They are universally compatible with just about every usage and storage medium imaginable, allowing for high quality photographic images at manageable sizes. Digital image files including JPEGs are often stored, transfered and used directly from today's most popular digital storage devices and mediums. These include memory cards (such as those found in cameras), memory sticks, cards, portable hard drives, internal hard drives, network storage devices, as well as DVDs and CDs.So when converting traditional photographic prints, slides and negatives to digital - what are the factors and options impacting digital file sizes and storage requirements? Generally, image size is a result of original media size, scanning resolution (dpi or dots/pixels per inch), image content, image processing(including compression) and file type.
The tables below (one for each scan resolution) show estimates of how, on average, various prints scans will be sized and the resulting storage requirements.
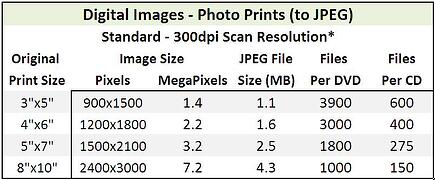
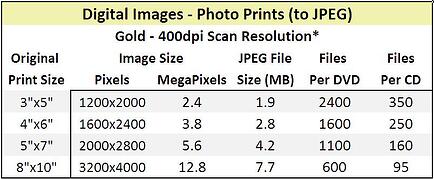
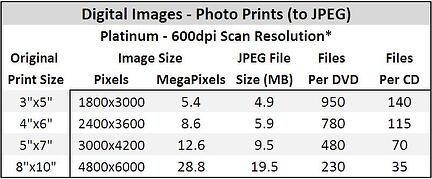
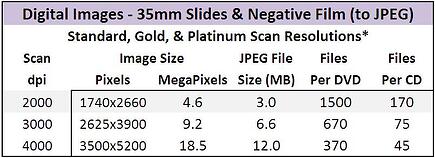
The table below shows estimates of how, on average, 35mm Slides and Negatives scans will be sized at three different scan resolutions and the resulting storage requirements.
The table below shows estimates of how, on average, 35mm Slides and Negatives scans will be sized at three different scan resolutions for TIFF files and the resulting storage requirements.
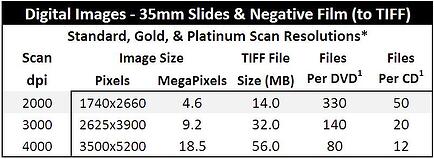
* Actual files sizes and capacities may vary significantly by file and on average based upon factors including media, condition, content, and processing options.
(1) Files per DVD and Files per CD are estimated for illustrative purposes only, the FotoBridge TIFF option may require and include mobile drive as transfer media.
(1)



